Supercritical adsorption of methane on active carbon
The applicability of the proposed adsorption isotherm equation was tested
for high - pressure adsorption isotherms of methane on active carbon Norit
R2, measured in our laboratory. 8
It was found that the isotherms for this system could not be described
by classical Langmuir equation in the entire pressure and temperature ranges
of the experimental data. Similar likes in Sircar’s work 9
linearized Langmuir plots exhibit considerable departure from linearity.
It is caused by heterogeneity of the carbon surface. 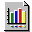 Figure 4 shows the results of fitting using Langmuir
isotherm equation. The circles and the solid lines represent the experimental
points and the model calculations, respectively. The goodness-of-fitting
was also determined by consideration the dispersion of residuals in fitting
experimental data.
Figure 4 shows the results of fitting using Langmuir
isotherm equation. The circles and the solid lines represent the experimental
points and the model calculations, respectively. The goodness-of-fitting
was also determined by consideration the dispersion of residuals in fitting
experimental data.  Figure 5 depicts the dispersion of errors for experimental
points.
Figure 5 depicts the dispersion of errors for experimental
points.
 Figure 4 Figure 4 |
Best-fit Curves for Langmuir Isotherm |
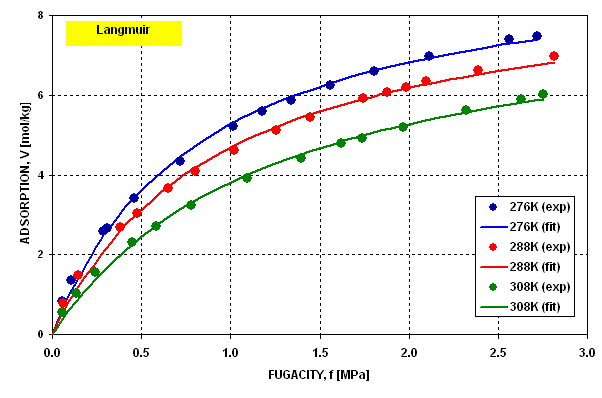
 Figure 5 Figure 5 |
Dispersion of Fitting Error for Langmuir
Isotherm |
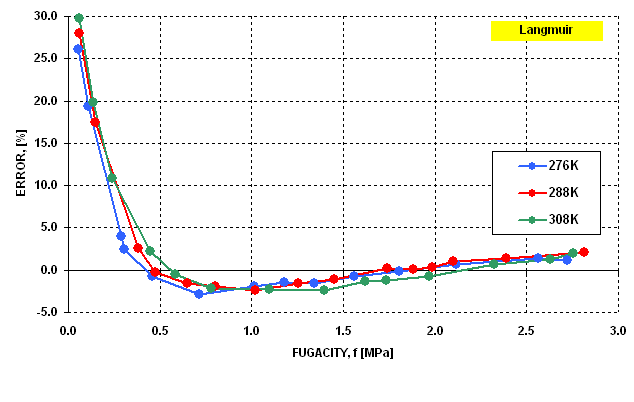
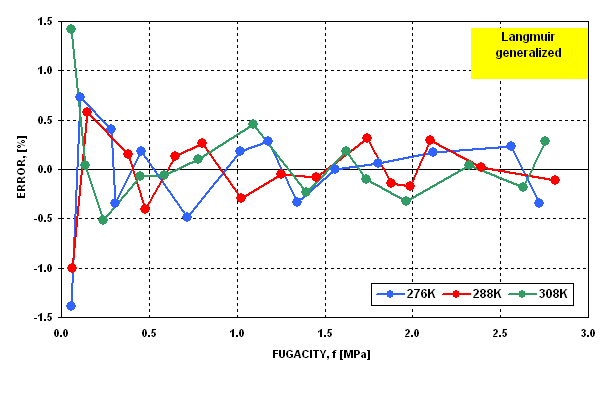
The modified Langmuir equation was then evaluated to determine how well
it represents the gas - solid equilibria. The results are presented in  Figure 6 and
Figure 6 and  Figure 7 . It may be seen that in the last case the dispersion
of error is statistically random and the error does not exceed the limit
of 1.5%.
Figure 7 . It may be seen that in the last case the dispersion
of error is statistically random and the error does not exceed the limit
of 1.5%.
 Figure 6 Figure 6 |
Best-fit Curves for Langmuir Generalized
Isotherm |
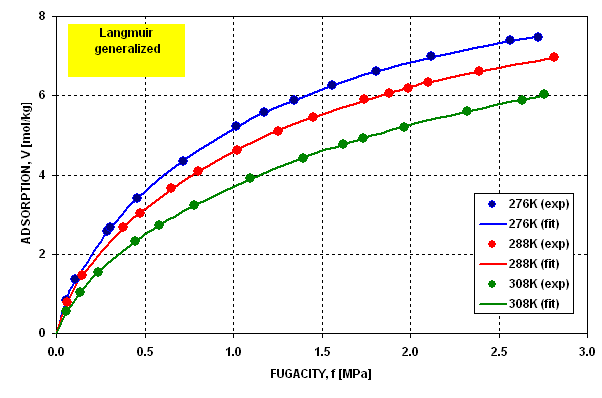
 Figure 7 Figure 7 |
Dispersion of Fitting Error for Langmuir
Generalized Isotherm |
 Table
2 summarizes the best-fit parameters for systems under investigation.
Henry’s-law constants at different temperatures (KH =
Vm /a) and isosteric heat of adsorption at zero coverage
calculated from the Henry’s-law constants (KH = Ko.exp(qo/RT)
are also listed in
Table
2 summarizes the best-fit parameters for systems under investigation.
Henry’s-law constants at different temperatures (KH =
Vm /a) and isosteric heat of adsorption at zero coverage
calculated from the Henry’s-law constants (KH = Ko.exp(qo/RT)
are also listed in  Table
2
Table
2
 Table 2 Table 2 |
Best-fit Parameters and Properties of System
Active Carbon - Methane Calculated from Langmuir Generalized Equation |
|
Best-fit parameters
|
T = 276K
|
T = 288K
|
T = 308K
|
|
Vm, [mol/kg]
|
2.459
|
2.430
|
2.381
|
|
a1.10-5
|
1.25
|
1.46
|
2.15
|
|
aL.10-5
|
5.55
|
6.95
|
9.89
|
|
n
|
4.2
|
4.1
|
4.1
|
|
Standard error of fit
|
0.0166
|
0.0120
|
0.0116
|
|
Henry's-law constant, KH.105 [mol/(kg
Pa)]
|
1.97
|
1.66
|
1.11
|
Henry's-law constant at 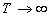 ,
Ko.108 [mol/(kg Pa)] ,
Ko.108 [mol/(kg Pa)]
|
6.53
|
|
Isosteric heat of adsorption at zero coverage, qo [kJ/mol]
|
13.2
|
The results presented show that the equation proposed can describe the
isotherm data quantitatively. The parameter Vm
varies slightly with temperature, which is consistent with the Langmuir
model. The value of isosteric heat of adsorption at zero coverage is higher
than the heat of condensation and is enough to be characterized as physical
adsorption.
 Figure 4
Figure 4
 Figure 5
Figure 5


 Figure 6
Figure 6
 Figure 7
Figure 7


