|
Home |
![]()
![]() WYKŁADY > PRZERÓBKA PLASTYCZNA METALI - KUŹNICTWO:
WYKŁADY > PRZERÓBKA PLASTYCZNA METALI - KUŹNICTWO:
1. Konstrukcja
odkuwki matrycowej
2. Dobór
płaszczyzny podziału
Kuźnictwo



![]() Zakłady
kuźnicze w Polsce - ZKP
Zakłady
kuźnicze w Polsce - ZKP
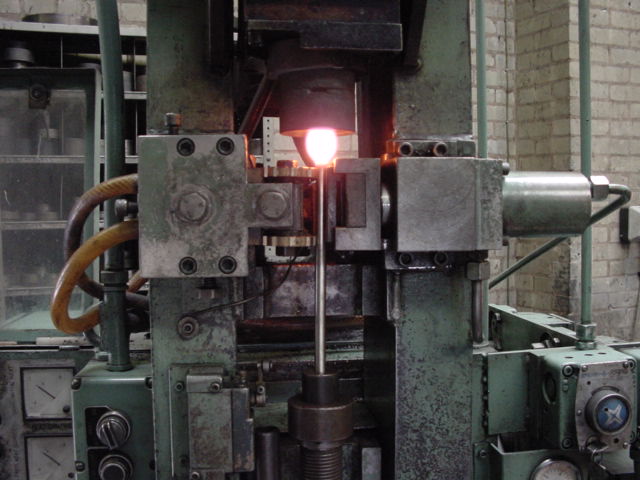
![]() Kucie matrycowe – SMS Eumuco
Kucie matrycowe – SMS Eumuco
![]()
![]() >
>![]() Brass Forgings
>
Brass Forgings
>![]() Aluminum Forgings:
Aluminum Forgings:



![]()
![]() Supercharger Turbine Blades; Gas Turbine Blades and Stators; Various
Forgings
Supercharger Turbine Blades; Gas Turbine Blades and Stators; Various
Forgings



![]() Odkuwki ze stopów Al (i innych stopów metali nieżelaznych):
Odkuwki ze stopów Al (i innych stopów metali nieżelaznych):



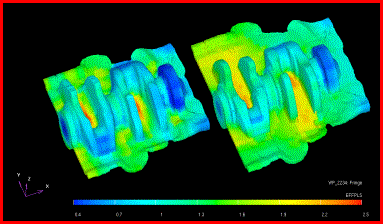

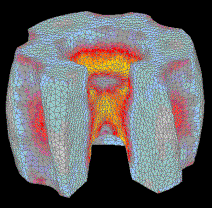
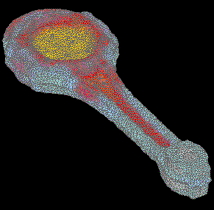
![]()
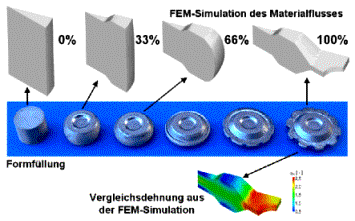
![]() Symulacja
procesów kucia matrycowego - OHIO: kliknij także na
obrazy:
Symulacja
procesów kucia matrycowego - OHIO: kliknij także na
obrazy:
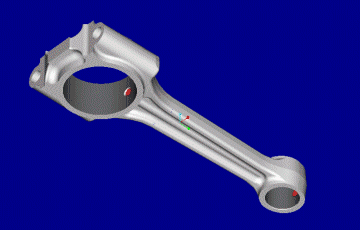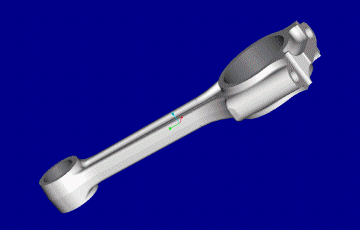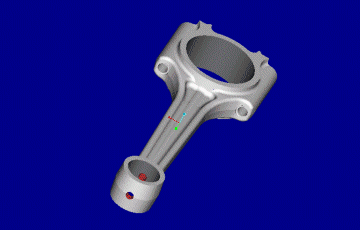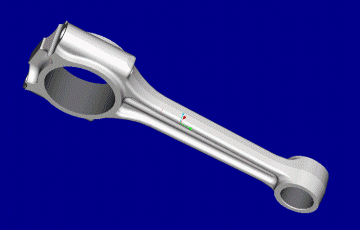
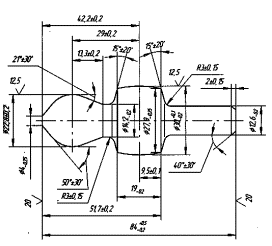
![]() Przykład rysunku wyrobu
gotowego i odkuwki
Przykład rysunku wyrobu
gotowego i odkuwki
![]() Kucie wałów korbowych metodą TR (Tadeusza
Ruta)
Kucie wałów korbowych metodą TR (Tadeusza
Ruta)
Metoda kucia TR polega na zastosowaniu przegubowego systemu zamiany nacisku
prasy na siły samoczynnie mocujące obrabiany pręt i siły kształtujące odkuwkę.
Urządzenia do kucia metodą TR są
uniwersalne i proste w konstrukcji. Mogą być instalowane na prasach
kuźniczych o nacisku do 100 MN;
a) Odkuwka wału korbowego podczas kucia metodą TR w
zakładach Krupp - Bochum, Niemcy;
b) Wykorbienie wału korbowego typu Sulzer
odkute w zakładach Japan Steel Works - Muroran Plant, Japonia
 a)
a)  b)
b)
![]() Kucie odkuwek w przyrządach kuźniczych
typu TR
Kucie odkuwek w przyrządach kuźniczych
typu TR


![]() Prasa PHPO 4000 do prasowania
obwiedniowego i części prasowane obwiedniowo
Prasa PHPO 4000 do prasowania
obwiedniowego i części prasowane obwiedniowo


![]() Prasa z wahającą
matrycą do prasowania obwiedniowego PXW100A (Prasa
Marciniaka)
Prasa z wahającą
matrycą do prasowania obwiedniowego PXW100A (Prasa
Marciniaka)
Kąt wychylenia
regulowany bezstopniowo; nacisk maksymalny 1600 kN

Zdzisław Marciniak z
Politechniki Warszawskiej jest jednym z najwybitniejszych fachowców
w dziedzinie teorii i praktyki plastycznej obróbki materiałów. Jego prasa z wahającą
matrycą, realizująca nową, całkowicie oryginalną
koncepcję techniczną, jest praktycznie zweryfikowanym osiągnięciem w skali
światowej. Produkuje się ją m.in. w USA, Szwajcarii, Chinach i Japonii.
Uczony jest członkiem PAN. Otrzymał doktorat honoris causa Politechniki
Warszawskiej.
![]() Manufacturing
(Photos) Haynes
International, Inc . HASTELLOY alloy; HAYNES
alloy
Manufacturing
(Photos) Haynes
International, Inc . HASTELLOY alloy; HAYNES
alloy
1) 2)
2)
1) Hot working hydraulic forge press
(lewa str. – manipulator
kuźniczy)
2) A key piece of equipment at the Openshaw, England bar facility
is the GFM-25 long rotary
forging machine
![]() Prasy śrubowe do kucia
matrycowego i inne (schematy) – SMS Eumuco
Prasy śrubowe do kucia
matrycowego i inne (schematy) – SMS Eumuco
![]() Młoty do kucia matrycowego
– SMS Eumuco >> Całość firmy
Młoty do kucia matrycowego
– SMS Eumuco >> Całość firmy
![]() Smary do
narzędzi kuźniczych – ZKP (video>
Smary do
narzędzi kuźniczych – ZKP (video>![]() Dag 2000 Servo
Reciprocator Video (5 meg))
Dag 2000 Servo
Reciprocator Video (5 meg))
![]() Rysunek matrycy z
ukształtowaną odkuwką
Rysunek matrycy z
ukształtowaną odkuwką
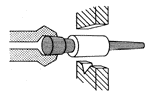
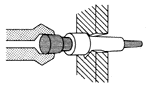
![]() Operacje kucia swobodnego - FIA
Operacje kucia swobodnego - FIA
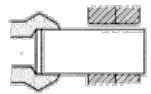
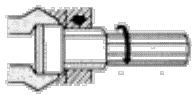
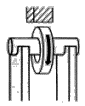
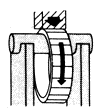
![]() Ogólne metody wytwarzania odkuwek - FIA
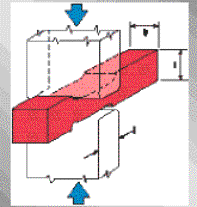
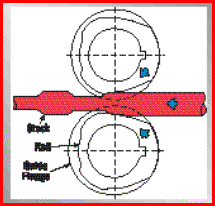
Ogólne metody wytwarzania odkuwek - FIA
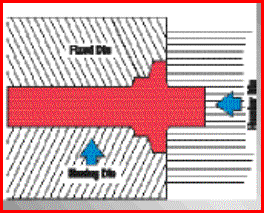
![]() Kucie matrycowe na prasach
(młotach) i kuźniarkach - FIA
Kucie matrycowe na prasach
(młotach) i kuźniarkach - FIA
K.
Siegert, D. Ringhand and R. Neher, Institut für Umformtechnik, Universität
Stuttgart; (17
pages, 18 figures)


![]() Podstawy
procesów kucia (klasyfikacja, skosy matrycowe, itp)
Podstawy
procesów kucia (klasyfikacja, skosy matrycowe, itp)
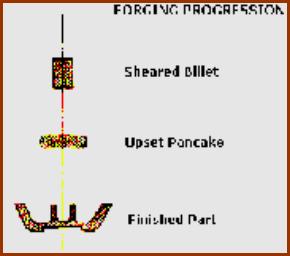
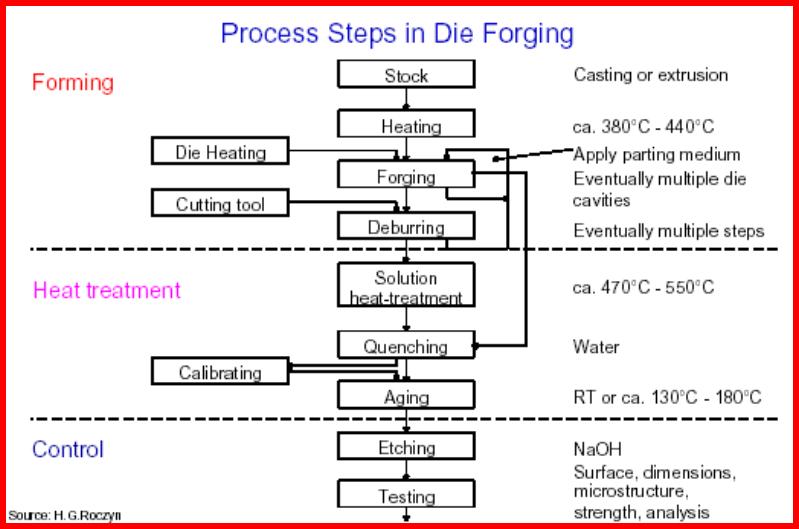
![]() FORGING
FORGING
...
These include open-die hammer forging, drop forging, upset forging, automatic hot forging, and roll
forging...

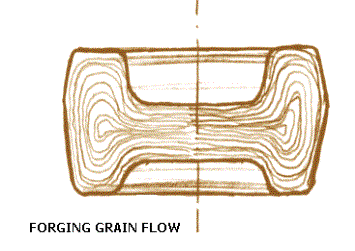
Układ
włókien (wydłużonych ziarn) ^ w odkuwce Kucie
matrycowe wielowykrojowe ^
K. Siegert, R. Malek and R. Neher, Institut für
Umformtechnik,Universität Stuttgart; (18 pages,
20 figures)
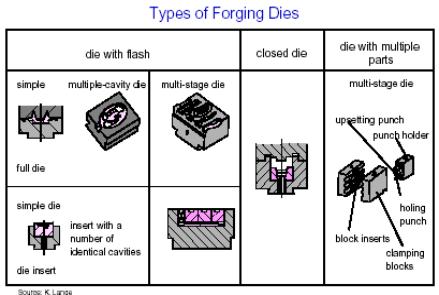

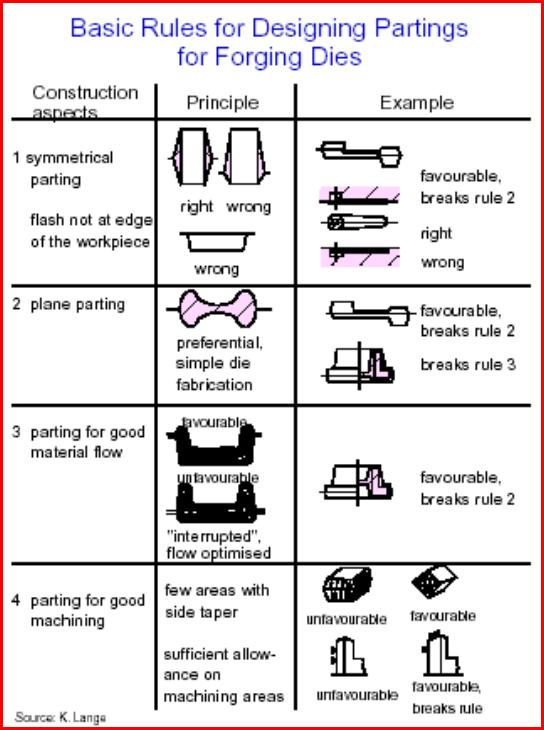
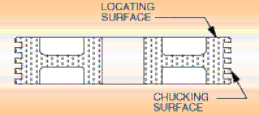
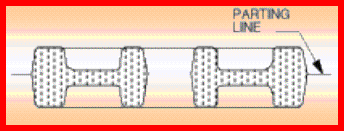
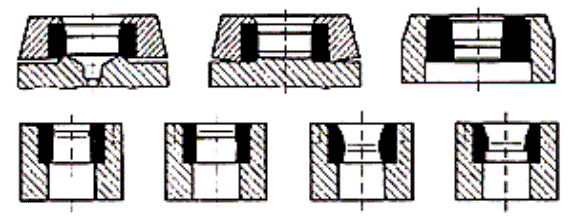
Projektowanie narzędzi – ustalenie optymalnego
położenia płaszczyzny podziału matryc:
![]() Design
Rules for Parts Made From Impression Die Forgings
Design
Rules for Parts Made From Impression Die Forgings
a)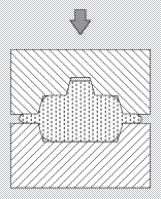 b)
b)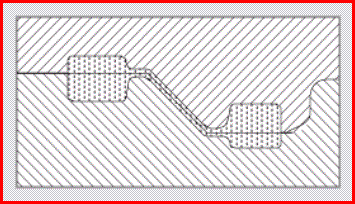
a) The most economical shape to forge is one that can be formed in impression moving in opposite directions.
b) The forging as oriented generates a side thrust
in the die requiring the counterlock to prevent
lateral shift of the die. The counterlock is subject to wear from the side load
c) d)
d)
c) The forging can be rotated in the die to balance
the lateral loads and eliminate the counterlock. However, the holes in the bosses cannot be forged, and must be
fully machined
d) Where production quantities justify two sets of
impression dies, the forgings can be oriented opposite to balance the
side loads. This arrangement permits the holes
in the bosses to be forged to reduce the amount
of machining required (najkorzystniejsze rozwiązanie położenia
płaszczyzny podziału matryc)
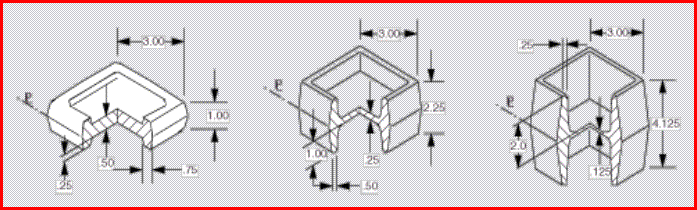
This figure represent shapes that are progressively more difficult to forge
prepared by K. Siegert, A. Möck and R. Neher, Institut für Umformtechnik,
Universität Stuttgart, Contents: 21 pages, 18 figures
![]() ! Uwaga
dla studentów: w projektach i pracach dyplomowych
wymagany jest poprawny zapis literaturowy > 1)
w przypadku opracowań tekstowych należy wymienić autorów, 2) zawsze należy
podać tytuł strony internetowej lub tytuł całego opracowania tekstowego, 3) nazwę firmy/instytucji będącej
właścicielem opracowanej strony, 4) internetowy adres:
! Uwaga
dla studentów: w projektach i pracach dyplomowych
wymagany jest poprawny zapis literaturowy > 1)
w przypadku opracowań tekstowych należy wymienić autorów, 2) zawsze należy
podać tytuł strony internetowej lub tytuł całego opracowania tekstowego, 3) nazwę firmy/instytucji będącej
właścicielem opracowanej strony, 4) internetowy adres:
Literatura (przykład
poprawnego zapisu !):
1. K. Siegert, A. Möck and R. Neher,
Forging Alloys,Institut für Umformtechnik, Universität Stuttgart,
http://www.aluminium.org/education/TALAT/lectures/3401.pdf
Spis treści (Forging
Alloys):
1 Aluminium Alloys
for Forging
Non-Heat-Treatable
Wrought Alloys; Heat-Treatable Wrought Alloys
2 Methods of
Improving Strength
Strain Hardening;
Solid Solution Hardening; Particle Hardening
3 Microstructure
Influence of Fiber
Structure; Defects due to Non-Uniform Flow
4 Forging Process
Data and Forging Properties
Characteristic
Temperatures for Certain Aluminium Forging Alloys
Characteristic
Mechanical Property Values for some Forged Alloys
Forging
Temperature and Die Temperature
Influence of
Temperature and Forming Rate on Flow Stress
5 Friction and
Lubrication; 6 In-Process Heat Treatment;
Literature
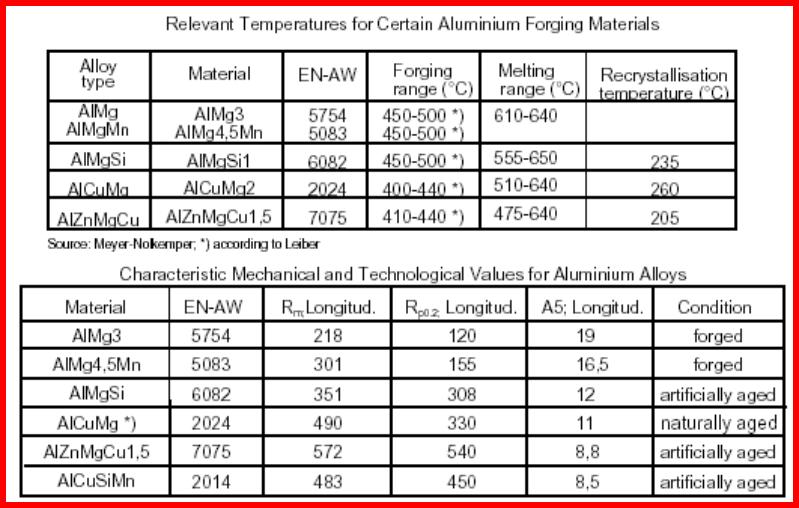
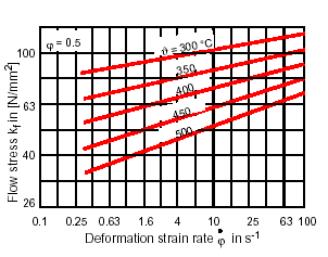
Flow Curves for AlMgSi1 Flow Curves for
AlCuMg2
(Cylinder Compression Test)






ARMOR CAR & TANK PARTS
(ROAD WHEEL & MISSION HOUSING) ARMOR
CAR & TANK PARTS ENGINE CON-ROD
& INDUSTRIAL MACHINERY PARTS



![]() Technologia wytwarzania
kuźniczego obręczy - FIA
Technologia wytwarzania
kuźniczego obręczy - FIA
 Heat-resistant,
high-strength discs:
Heat-resistant,
high-strength discs:
The turbine discs used in aircraft engines require the
utmost reliability and safety. In addition to our accumulated expertise in the
development of alloy design down to metal forming, Mitsubishi Materials has
employed its computer simulation technology to develop the technology for microstructure prediction using numerical analysis. This prediction technology pursues developments in near -net shaping and establishes
thermo-mechanical control forging technology to achieve the highest quality.
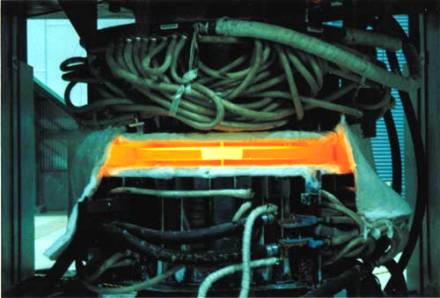

Hot forging byhydraulic press (Okegawa Plant) Microstructure analysis of disk forging
process
![]()
(i inne wyroby ze
stopów Cu otrzymane kuciem na zimno)





![]() Using Cold Metal Forming to Improve Products and Increase Added Value
Using Cold Metal Forming to Improve Products and Increase Added Value
 BCFG Library:(The Bela Lengyel Collection)
BCFG Library:(The Bela Lengyel Collection)
![]() ATLAS OF HOT WORKING
PROPERTIES OF NON FERROUS METALS - Volume 1. Aluminium and Aluminium
Alloys, Volume 2 Copper and Copper Alloys. Published by the Deutsche
Gesellschaft fur Metallkunde E.V., 1978.
ATLAS OF HOT WORKING
PROPERTIES OF NON FERROUS METALS - Volume 1. Aluminium and Aluminium
Alloys, Volume 2 Copper and Copper Alloys. Published by the Deutsche
Gesellschaft fur Metallkunde E.V., 1978.
![]() J. M. Alexander: STRENGTH OF MATERIALS - Volume I: FUNDAMENTALS, Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, 1981.
J. M. Alexander: STRENGTH OF MATERIALS - Volume I: FUNDAMENTALS, Ellis Horwood Ltd., Chichester, 1981.
![]() J. M. Alexander & R. C. Brewer: MANUFACTURING PROPERTIES OF
MATERIALS, D. Van Nostrand Company Ltd., London, 1963.
J. M. Alexander & R. C. Brewer: MANUFACTURING PROPERTIES OF
MATERIALS, D. Van Nostrand Company Ltd., London, 1963.
![]() J. M. Alexander & B. Lengyel: HYDROSTATIC EXTRUSION, Mills & Boon Ltd.,
London, 1971.
J. M. Alexander & B. Lengyel: HYDROSTATIC EXTRUSION, Mills & Boon Ltd.,
London, 1971.
![]() B. Avitzur: METALFORMING: PROCESSES AND
ANALYSIS, McGraw-Hill Series in Science and Engineering, 1968.
B. Avitzur: METALFORMING: PROCESSES AND
ANALYSIS, McGraw-Hill Series in Science and Engineering, 1968.
(itd.)




Aircraft Rivets, Automotive,
Bifurcated Rivets, Specials Self Piercing Rivets, Semi Tubular Rivets



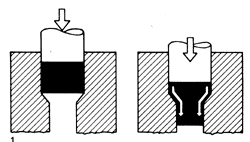
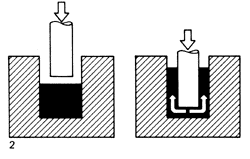
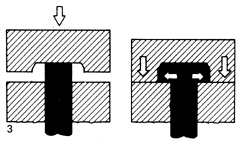
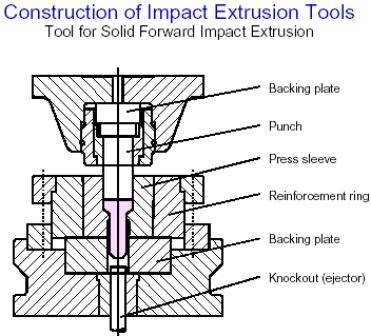
![]() Impact
Extrusion Processes
Impact
Extrusion Processes
Contents: 26 pages, 35 figures

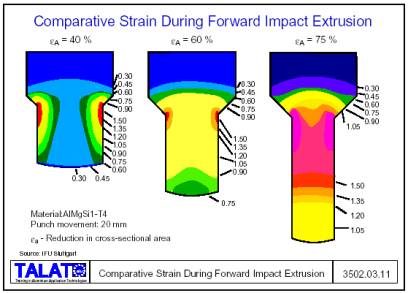
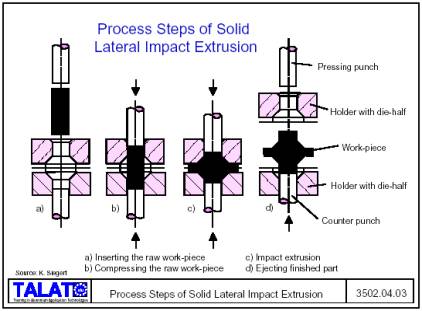
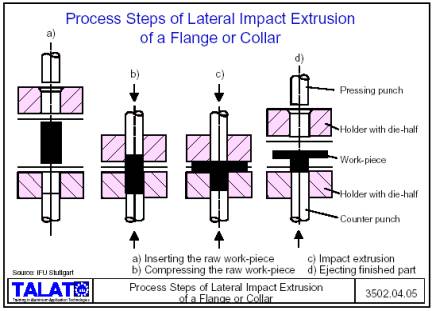
![]() Finishing
and other Supplementary Operations
Finishing
and other Supplementary Operations
Contents: 8 pages, 7 figures

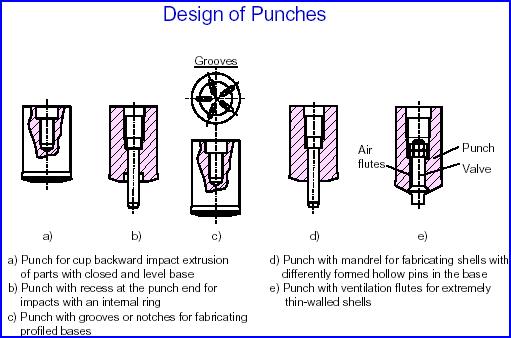
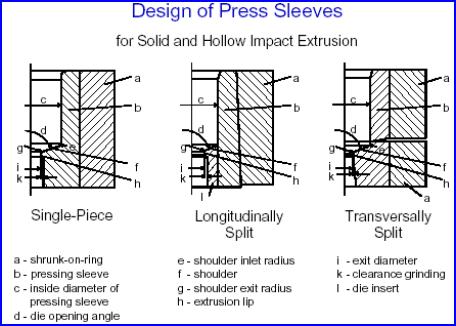
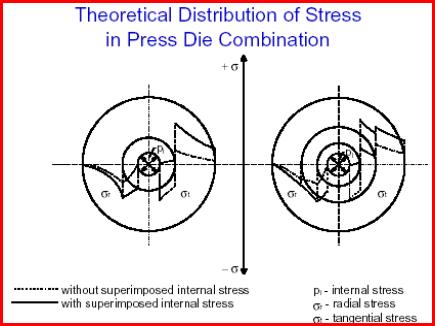
![]() Impact
Extrusion Design Aspects and Properties
Impact
Extrusion Design Aspects and Properties
Contents: 11 pages, 11 figures
Zasady projektowania narzędzi:
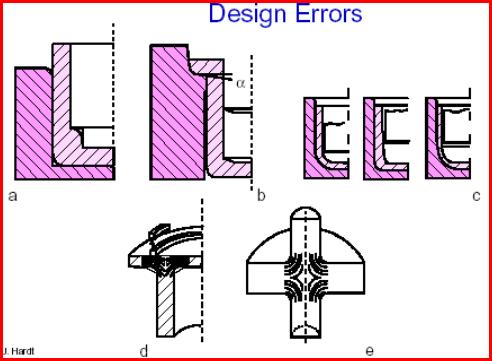 Avoid
using punches with recesses having right
angles or sharp edges and corners (a).Very
narrow shoulder angles lead to cracks in
the impact (b).The types of punch forms shown in Fig c are
to be avoided, especially for thin-walled parts. Forward
impact extruded parts with thin flanges should not have any
sharp-edged protrusions in the immediate vicinity of the region
with the largest deformation strain, since the material flows past these
protrusions without filling them (d). If a
flange is designed with two strands in the same axis, then the high shear
stresses that occur in the core of the work-piece can cause a hole
to be created here (e).
Avoid
using punches with recesses having right
angles or sharp edges and corners (a).Very
narrow shoulder angles lead to cracks in
the impact (b).The types of punch forms shown in Fig c are
to be avoided, especially for thin-walled parts. Forward
impact extruded parts with thin flanges should not have any
sharp-edged protrusions in the immediate vicinity of the region
with the largest deformation strain, since the material flows past these
protrusions without filling them (d). If a
flange is designed with two strands in the same axis, then the high shear
stresses that occur in the core of the work-piece can cause a hole
to be created here (e).
Contents: 10 pages, 10
figures
![]() Prediction
and Elimination of Defects in Cold Forging Using Process Simulation (
Altan,
T. and Hannan, D.)
Prediction
and Elimination of Defects in Cold Forging Using Process Simulation (
Altan,
T. and Hannan, D.)
10th Int. Cold Forging Congress, Sept 13-15,
2000, Stuttgart
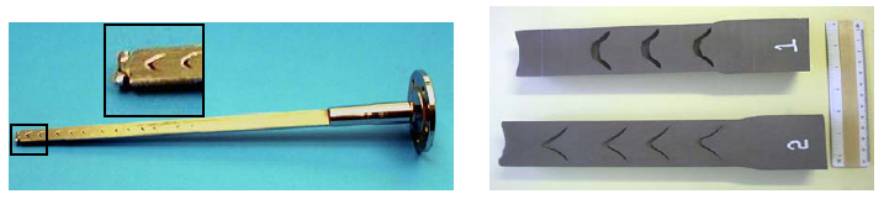
Automotive axle shaft with
chevrons configurations ^
Illustration of different chevron ^
 Umformen von
dichtereduzierten und kriechfesten Magnesiumlegierungen Prof.
Dr.-Ing. Eckart Doege
Umformen von
dichtereduzierten und kriechfesten Magnesiumlegierungen Prof.
Dr.-Ing. Eckart Doege
Präzisionsgeschmiedetes
Kettenritzel
(i także)![]() Umformung von Magnesiumknetlegierungen
Umformung von Magnesiumknetlegierungen ![]() Umformung von Aluminiumknetlegierungen
Umformung von Aluminiumknetlegierungen
![]() Precision
Forging of Magnesium Wrought Alloys
Precision
Forging of Magnesium Wrought Alloys

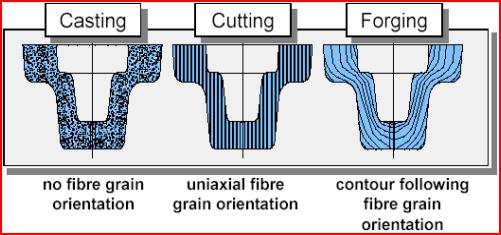
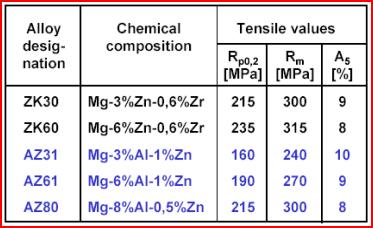
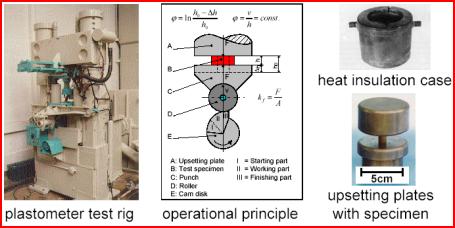
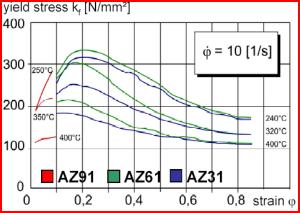
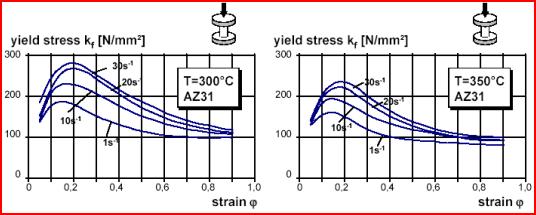
![]() Massivumformung (
Massivumformung (![]() Lehrstuhl für
Fertigungstechnologie )
Lehrstuhl für
Fertigungstechnologie )

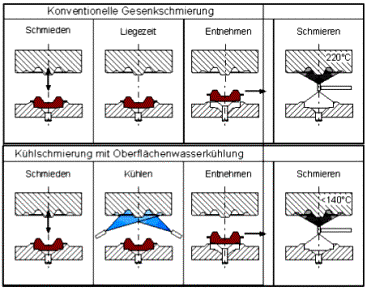
![]() Untersuchungen zu alternativen
Untersuchungen zu alternativen
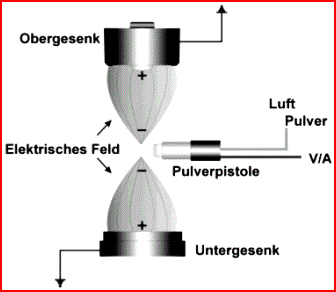
![]() Materials
for precision forging
Materials
for precision forging ![]() Hard
finishing of precision forges components
Hard
finishing of precision forges components

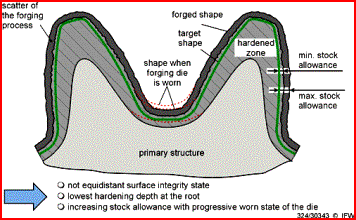
Wyroby
kuźnicze (odkuwki swobodne i matrycowe)
![]() Odkuwki matrycowe stalowe i ze
stopów tytanu i aluminium - StalPlast
Odkuwki matrycowe stalowe i ze
stopów tytanu i aluminium - StalPlast
![]() Galeria wyrobów kuźniczych I –
FIA
Galeria wyrobów kuźniczych I –
FIA
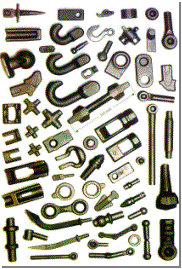



![]() Galeria wyrobów kuźniczych II –
FIA
Galeria wyrobów kuźniczych II –
FIA
![]() Zastosowanie wyrobów kuźniczych
- FIA
Zastosowanie wyrobów kuźniczych
- FIA
![]() Odkuwki matrycowane
spęczaniem
Odkuwki matrycowane
spęczaniem ![]() High-performance
materials:
High-performance
materials:
Precision
forgings


![]() Stopy aluminium wykorzystane
do kucia odkuwek - FIA
Stopy aluminium wykorzystane
do kucia odkuwek - FIA
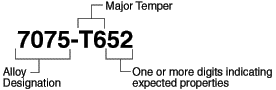
![]() Prawidłowe oznaczenie materiału odkuwki
(zgodne z nowymi polskimi normami
- EN PKN)
Prawidłowe oznaczenie materiału odkuwki
(zgodne z nowymi polskimi normami
- EN PKN)
1) gatunku stopu
Al i 2) jego stanu po obróbce
cieplnej: 7075-T652
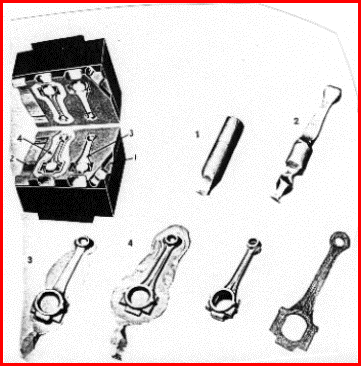
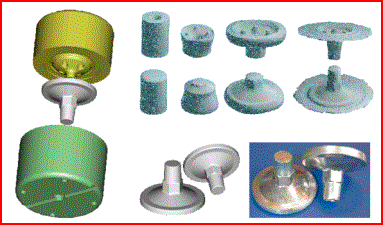
 Forged end-products gallery
Forged end-products gallery

Przykład bardzo dużej odkuwki matrycowej ze stopu tytanu
(przegroda odrzutowca – „F-22 aircraft”)
![]() Stopy miedzi wykorzystane do
kucia odkuwek - FIA;
Stopy miedzi wykorzystane do
kucia odkuwek - FIA;
![]() Stopy tytanu wykorzystane do
kucia odkuwek - FIA
Stopy tytanu wykorzystane do
kucia odkuwek - FIA
![]() Stopy niklowe i kobaltowe
wykorzystane do kucia odkuwek - FIA
Stopy niklowe i kobaltowe
wykorzystane do kucia odkuwek - FIA
Specjalne
procesy kuźnicze
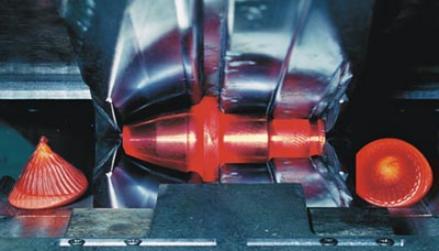
![]() Technology processes of wedge rolling and the
tools
Technology processes of wedge rolling and the
tools
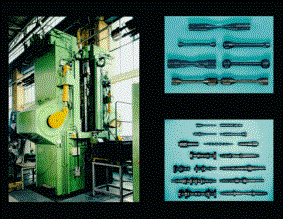
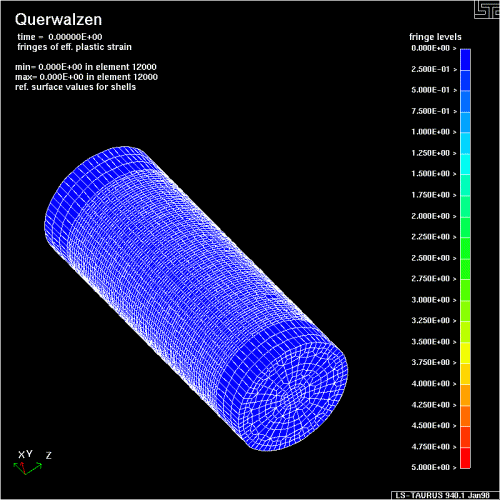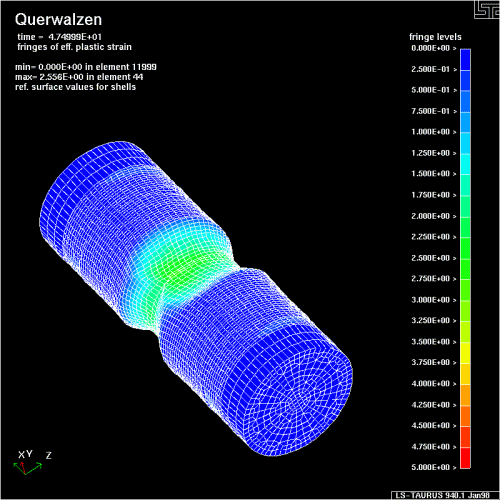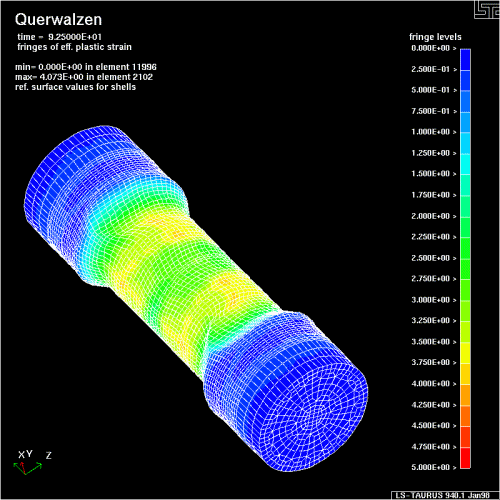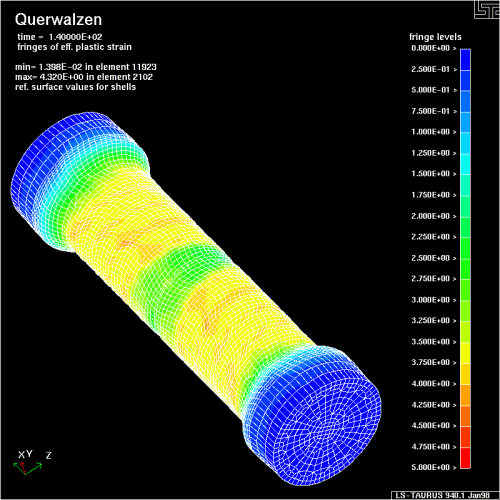
Walcowanie poprzeczne (klinowe) na zimno i gorąco
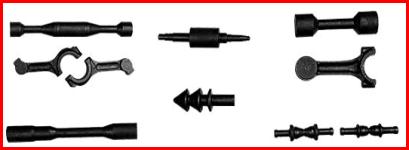
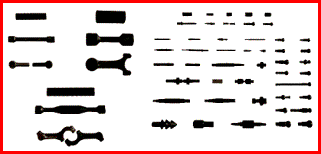
![]()
![]() Flachbackenquerwalzen
(Walcowanie poprzeczne płaskimi narzędziami)
Flachbackenquerwalzen
(Walcowanie poprzeczne płaskimi narzędziami)
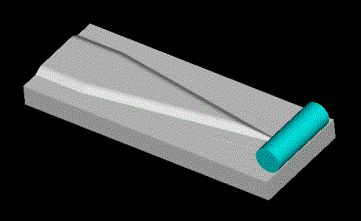
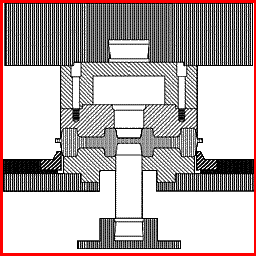
Operacje
pomocnicze procesu kucia matrycowego
![]() Rysunki jednoczesnego
okrawania wypływki i denka – stopy kuźnicze (obr.:Corel_Krzywa
tonalna)
Rysunki jednoczesnego
okrawania wypływki i denka – stopy kuźnicze (obr.:Corel_Krzywa
tonalna)
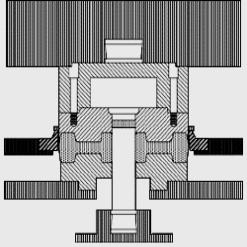
Completion of the trim and pierce operation
Jednoczesne okrawanie wypływki i denka
Ogólne łącza:
![]() Broszura_Rozdziały:
NEAR NET SHAPE COLD, WARM AND
HOT FORGING
Broszura_Rozdziały:
NEAR NET SHAPE COLD, WARM AND
HOT FORGING
![]() CLOSED
DIE HOT FORGING WITH FLASH
CLOSED
DIE HOT FORGING WITH FLASH
![]() CLOSED
DIE HOT FORGING WITH FLASH
CLOSED
DIE HOT FORGING WITH FLASH
![]() Słownik określeń
kuźniczych (GLOSSARY OF FORGING TERMS)
Słownik określeń
kuźniczych (GLOSSARY OF FORGING TERMS)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() WYKŁADY > PRZERÓBKA PLASTYCZNA METALI - KUŹNICTWO:
WYKŁADY > PRZERÓBKA PLASTYCZNA METALI - KUŹNICTWO:
1. Konstrukcja
odkuwki matrycowej
2. Dobór
płaszczyzny podziału
|
Home |
![]()
Aktualizowano:
2003-10-22