Spatial data stored in files
There are a large number of spatial data formats. Initially, one feature object class was saved in the w directory as a set of approximately 20 files. Then the number of files was reduced to several and the object class was stored in 4 files. Then, the introduction of hybrid spatial object saving. Vector files contained geometry and relational databases attributes of objects.
Spatial data in relational database systems
The storage of spatial data in relational databases started with the new BLOB and SDO_Geometry data types. Such data storage enables the integration of spatial data with descriptive data
Open Source Solutions
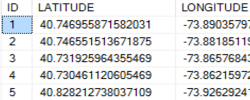
WKB is the key structure of the BLOB data type that stores the geometry of the vectors data in the database. It is used in Spatilite, PostgreSQL and other databases.
Comercial Solutions
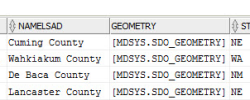
Programs such as ArcGIS or Geomedia also use the BLOB data type to store data, but the data structure is closed and unpublished. Oracle created the type SDO_Gemoetry, which has been publicly available to read and write methods.
