Science Education through Earth Observation for High Schools (SEOS)
Remote Sensing Tutorials, Government of Canada NRCAN
Hejmanowska B. 2014 Remote sensing and photo-interpretation
Sample modules used in class: python, numpy, scipy, matplotlib, PIL, rasterio, scikit-image, scikit-learn
Sentinel satellite image: Level-1c, Level-2a, Level-2a product-formatting
General definition of Remote Sensing is “the science and technology by which the characteristics of objects ofinterest can be identified, measured or analyzed the characteristics without direct contact” (JARS, 1993).
Usually, remote sensing is the measurement of the energy that is emanated from the Earth’s surface. If the sourceof the measured energy is the sun, then it is calledpassive remote sensing, and the result of this measurement canbe a digital image (Richards and Jia, 2006). If the measured energy is not emitted by the Sun but from the sensor platform then it is defined as active remote sensing, such as radar sensors which work in the microwave range(Richards and Jia, 2006).
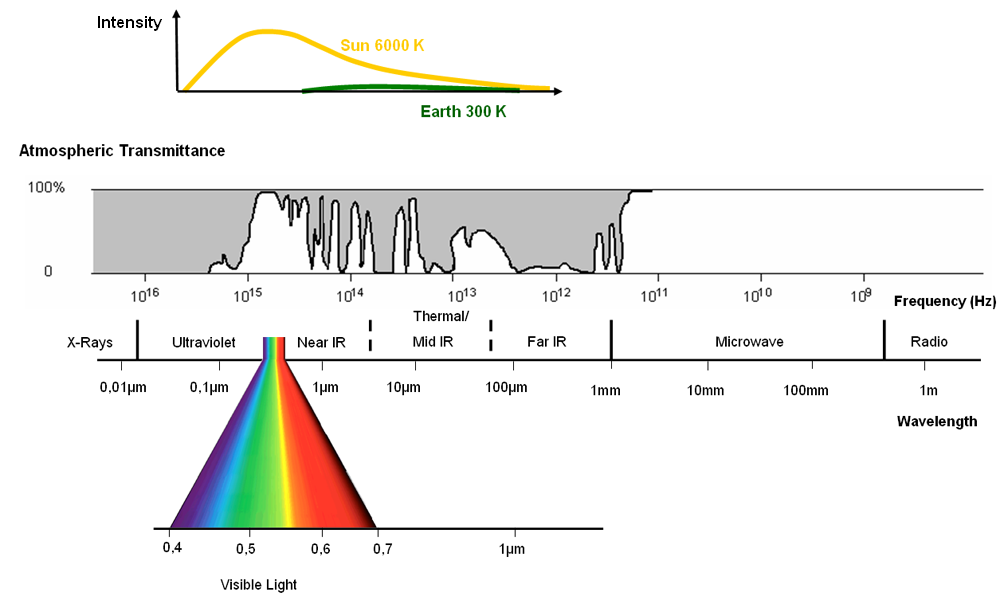
The electromagnetic spectrum is “the system that classifies, according to wavelength, all energy (from shortcosmic to long radio) that moves, harmonically, at the constant velocity of light” (NASA, 2013).
Passive sensors measure energy from the optical regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: visible, near infrared (i.e. IR), short-wave IR, and thermal IR.
Gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet, visible, near and mid-infrared, thermal, radar, radio waves
Electromagnetic spectrum and atmospheric permeability Source: Albertz 2007 after modifications for SEOS
A matrix consisting of rows (r - rows) and columns (c - cols).
An element of the matrix (a cell) is called a pixel.
In a pixel is stored a numerical value (DN - digital number), called pixel brightness, which depends on the amount of radiation falling on the pixel.
tutorialspoint image processing
The size of an image depends upon three things.
The formula for calculating the size is given below.
Size of an image = rows * cols * bpp
Assuming it has 1024 rows and it has 1024 columns. And since it is a gray scale image, it has 256 different shades of gray or it has bits per pixel. Then putting these values in the formula, we get
Size of an image = rows * cols * bpp
= 1024 * 1024 * 8 = 8388608 bits.
But since its not a standard answer that we recognize, so will convert it into our format.
Converting it into bytes = 8388608 / 8 = 1048576 bytes.
Converting into kilo bytes = 1048576 / 1024 = 1024kb.
Converting into Mega bytes = 1024 / 1024 = 1 Mb.
Thats how an image size is calculated and it is stored. Now in the formula, if you are given the size of image and the bits per pixel, you can also calculate the rows and columns of the image, provided the image is square(same rows and same column).
Spatial - size of the pixel in the field
Spectral - number of spectral channels
Radiometric - number of bits / one pixel
Temporal - how often the image is recorded
How to calculate how many different numbers can be stored in a pixel, and what it says on that value?
How do you calculate the size of a raster file on disk?
People and story behind Neptune
neptune.ai image-processing-python
Radiation as a function of wavelength for objects with different absolute temperatures. Source: ESA Eduspace after modifications for SEOS
Planck's - dependence of radiation energy on wavelength
Wien - as the temperature of a body decreases, the maximum radiation shifts to longer wavelengths (cf. Earth and Sun)
Stefan-Boltzman - determines the total energy radiated by a body over the entire wavelength range
Kirchoff - the ability to absorb (saturate) radiation is the same as the ability to emit it
Interaction of radiation with the atmosphere and with the Earth's surface
"All ranges of radiation are affected by the atmosphere in many different ways. Solar radiation, like Earth's reflected radiation, is scattered, reflected or absorbed by particles in the atmosphere. Clouds are the biggest obstacle to radiation and prevent passive satellite sensors from measuring the Earth's surface." (SEOS)
Why the sky is blue ?
Definition of reflectance, transmissivity, emissivity (absorption). In remote sensing we can record reflected (scattered) and emitted radiation, we cannot record transmitted and absorbed radiation.
"Kirchoff's law, developed in 1859, states: α=ε, the absorption and emission capacity are the same. Therefore, objects that absorb all of the incident radiation (α=1) have the highest ability to give off thermal energy (ε=1). These are referred to as perfectly black bodies, where the term black indicates the complete absence of reflected radiation. Objects that absorb even a fraction of the incident radiation (α<1) are referred to as perfectly gray bodies.
The absorption and emission capabilities are wavelength dependent for a given body/object. A high or low absorption capacity of an object in different spectral ranges translates into a high or low emission capacity in the same spectral ranges. Therefore, the generalized Kirchoff's law can be written as: αλ=ελ" (after SEOS)
Reflection and scattering (after SEOS)
What does the amount of radiation reaching the sensor depend on?
Geometric corrections - fitting the image into a coordinate system (giving georeferencing) - transformations: Helmert, affine, projective or creating orthophotos using numerical terrain model (NMT)
Schematic representation of the geometric correction process (SEOS)
Image preprocessing
Extracting information from images
Pre-processed image
Image after "contrast stretching
Histogram before and after contrast stretching
The principle of linear contrast stretching
(per ILWIS stretch)
Panchromatic image (PAN) - in a wide range of visible radiation
Each COLOR can be created from the components of 3 colors: RGB Three spectral channels of a multispectral image can be used simultaneously
Composition in natural colors: channel B - color B, channel G - color G, channel R - color R
False Color Composite (FCC) channel G - color B, channel R - color G, channel IR - color R
Composite in natural colors and FCC
Classification process (Modified from: Naumann 2008, after SEOS)
read:
Selecting the training fields
Class separability analysis
Classification algorithms
x - classified pixel (class "a" or class "b" ?)
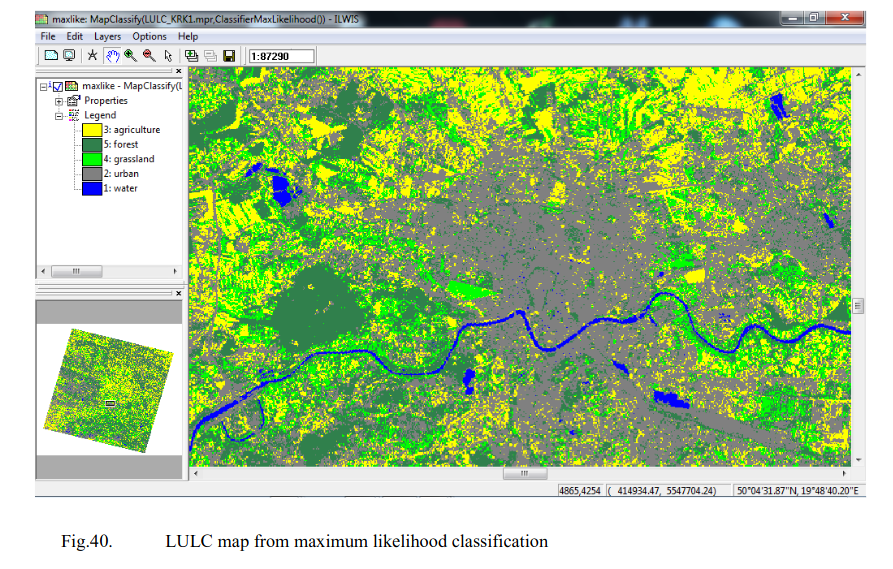
Classification result - land cover/land use map (LULC, Landuse / Landcover
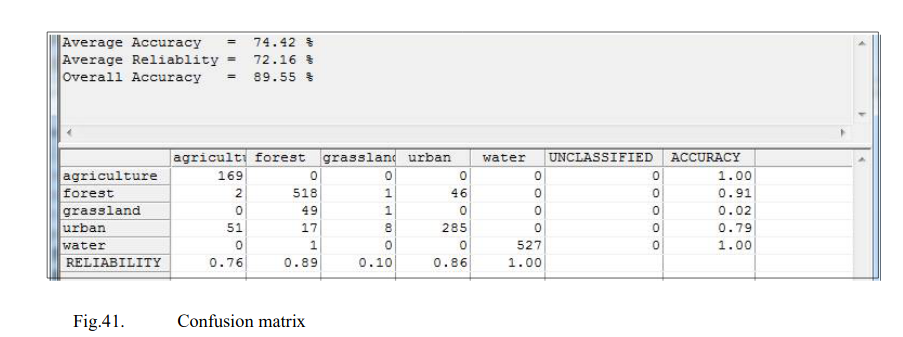
Confusion matrix analysis of classification result reliability