Software: Geomedia Professional, Geomedia Grid, Idrisi
Faculty: Mine surveying and Environmental Engineering
Direction: Environmental Engineering Specialization: Environmental Monitoring IV th year (7th and 8th semester), about 30 students/year
Introduction to GIS, definitions, examples, appications. Real word and GIS, type of presentation, weeknes of discrete model. Data gathering, data type, formats, size. GIS models: raster, vector. Vector model: spaghetti, object, topological. CAD and GIS. Coordinate system (polar, Cartesian). Referense ellipsoid. Geographical, geocentric coordinate system. Projections (TM, UTM). Official coordinate systems and projection in Poland (1942, 1965, 1992, 2000), definition, deformations, parameters. GIS data in internet. Introduction to Geomedia Professional, geoworspace and warehouse, object visualization, attribute querry.
Project1 – vector analyze: “Localization analyze for a new waste area”. Conditions for waste area localization: distance from water, roads and urban area, excluding existing land use area (urban, forest etc.). Minimum area analyze. Attribute querry, buffer, overlay, geometry information - Geomedia Professional functions.
Project2 – raster analyze: “Localization analyze for a new waste area”, according above mentioned conditions. Introduction to GeoMedia Grid, study area, import file, feature class resterizations. Recode, grid calculator, group, area – Geomedia Grid functions.
Project3 – comparison of Project2 and Project2.
Project4 – vector/raster analyze: developing of Project1/2, using DTM – exclude steep and west facing area. Slope, aspect generations, recode, vectorize to feature class – Geomedia Grid functions. Final vector analyze, choose optimal areas for waste localization.
Project5 – vector/raster analyze: “Flood area generation”. Digitalization of point on the river for hydraulic models calculation. Profile line generation in calculation points. Profile line rasterization. Water surface generation – interpolation. DTM – import. Reproject to water surface generation. Difference map generation = DTM – water surface. Flood area generation, recode – flood area = 1. Vectorize to feature class. Flood area analyze with regional GIS in Krakow in Geomedia Professional.
Project6 – vector.raster analyze: “Least cost new road generation”. Fuzzy condition: the less steep the better. Barriers: not urban or forest area, distance from roads and water.
Project7 – vector/raster analyze: “Agroclimatic zones”. Basing of DTM, rain maps. Temperature map generation from DTM (grid calculator). Temperature zones generation. Moisture map and zones generation.
Project8 – cartography – international map sheets. Map scale, name and size, Topographical and thematic maps. Hydrological map of Poland, Sozological Map of Malopolska Region. Cartographical presentation, generalization.
Project9 – GIS analyze basing on regional GIS – individual projects.


Site location - Krakow Poland - details
Application of geoinformatics
Practice: 96h/year
Software: Geomedia Professional, Geomedia Grid, Geomedia Terrain, MGE Terrain Analyst, PCI Geomatics, Envi
Faculty: Mine surveying and Environmental Engineering
Direction: Geodesy and Cartography Specialization: Geoinformatics, photogrammetry and remote sensing IV th year (after 8th semester), about 30 students/year
Project 1 : Generation of Digital Elevation Model applying different methods

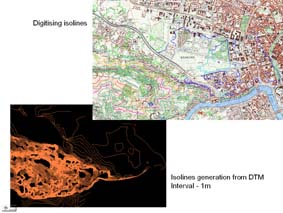
Project 2 : Estimation of Digital Terrain Model accuracy
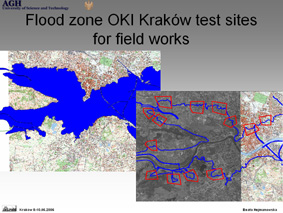
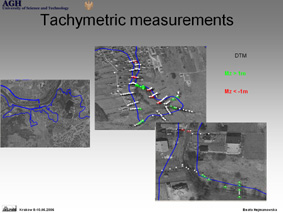
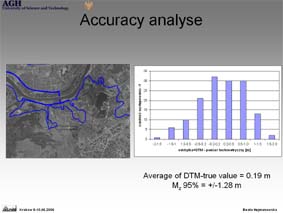
Project 3 : Field check of land use/land cover accuracy

