Computer simulations ...
Here, you can download educational programs demonstrating simulations of
various physical phenomena. Programs authors are Zbigniew Kąkol and
Jan Żukrowski.
All programs, available on this page, are distributed under
the Creative Commons
Non-Commercial license: Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0).
This software (all programs) is provided as is. This software has been written
with great care but we do not warrant that the software is error free. In no
event shall we, the authors, be liable for any consequential, special,
incidental or indirect damages of any kind arising out of the performance or use of this software.
Click below on the program name to download it.
Motion with constant acceleration
This program shows motion (along straight line) with constant acceleration
as a function of initial velocity and acceleration.
You can trace instantaneous velocity, position and displacement of a moving object. |
Projectile motion
This programs shows projectile motion as a function of
initial velocity and launch angle. Instantaneous velocity and acceleration (and their components) are displayed. |
Work done by a variable force
The program illustrates calculation of the work done by
a variable force F(x) which changes with distance. In program you can divide
displacement into short segments. In the limit, as the segments becomes very
small, we get a definite integral (are under F(x)), which we define to be the work W. |
One dimensional collisions
This program illustrates one dimensional collision
between two balls. You can adjust initial velocity of colliding balls, their mass m and coefficient of restitution. |
Two dimensional collisions
This program shows two hard balls colliding, one moving and one at rest.
You can adjust initial velocity of the striking ball, ratio of masses and impact parameter. |
Simple harmonic motion
This program illustrates a motion of a mass suspended
on a spring. You can adjust spring constant k, mass m and the amplitude of
the motion. Watch the changes of displacement, velocity, kinetic energy, potential energy, and total energy. |
Damped simple harmonic motion
Watch simple pendulum motion as a function of pendulum
length, motion amplitude, and damping constant. You can change option to critical damping or aperiodic motion. |
Superposition of waves
This program displays a result of superposition of two transverse waves as a function of amplitude ratio and phase shift.
Additionally you can watch standing waves and beats. |
The Doppler effect
This program shows Doppler effect for sound waves in the case when source and receiver move either
directly toward or directly away from each other, at speeds less than the speed of sound. You can change
speed of the source and receiver as well as source frequency. |
The Maxwell speed distribution
This program plots the Maxwell speed distribution for a given temperature.
You can compare plots generated for two selected temperatures. |
Diffusion
This program illustrates mixing of two gases, initially placed in two containers,
as a function of the temperature. In the program you can trace actual concentration
of gases and molecules speed distribution compared with the Maxwell speed distribution. |
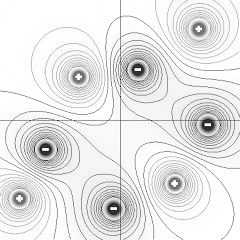
Electrostatics
This program shows electric field lines and electric potential due to given static configuration of point charges.
You can select particular charge configuration or create your own charge arrangement. |
Charge particle path in the magnetic field
This program shows charged particle path in uniform
magnetic field B. You can adjust magnitude of magnetic field B, particle velocity v, and angle between v and B. |
RLC series circuit
This program simulates voltage drops across each element of the circuit R, L, C
in comparision with applied voltage U(t) and the current I(t). The circuitt parameters: R, L, C and a frequency f of
applied voltage may be changed. Particularly, you can adjust either the frequency f of the source or natural frequency
of the circuit (by changing L and C) to reach the resonance state. |
Reflection and refraction of light
This program illustrates the direction of the incident, reflected, and refracted rays
at a flat and smooth interface surface between two materials in terms of the angle
of incidence and refractive indexes n1 i n2. |
Lenses
This program illustrates ray tracing method for image formation by converging and diverging lenses.
Using proper control you can change position of lens and object. You can also change focal length. |
Interference of light
With this program you can examine interference of two coherent light waves resulting
from sending a wave through two very narrow slits.
You can change a distance between slits, wavelength, and a distance from slits to screen. |
Single-slit diffraction
This program displays the diffraction pattern of plane waves of light that are diffracted by a single slit.
You can change a width of a slit, wavelength, and a distance from slit to screen. |
Double-slit diffraction
This program displays the diffraction pattern of plane
waves of light that are diffracted by two slits. You can change a distance
between slits, wavelength, a width of a slits, and a distance from slits to the screen. |
Electromagnetic wave model
This program illustrates plane polarized electromagnetic wave,
which propagates in Y direction. The electric field vectors E, are parallel to the Z axis,
whereas the vectors of the magnetic field B, are parallel to the X axis.
You can adjust wave lenght and amplitude of the fields. |
Blackbody radiation
The program plots blackbody radiation spectrum for a given temperature.
You can compare plots generated for two selected temperatures. |
Photoelectric efect
This programm visualizes the photoelectric effect experiment with photocell circuit.
In program, you can adjust a voltage placed across the electrodes of photocell, light intensity,
and light frequency (in the visible and ultraviolet range).. |
Wave functions of hydrogen atom
This program plots (for selected quantum numbers n, l, m) the radial part of hydrogen atom,
the radial and angular probability distribution function, and the visualization of hydrogen atomic orbitals
in two dimensions. |
Radioactive decay
The program illustrates spontaneous transformation of radioactive nuclei.
You can watch how the number of radioactive nuclei in
the sample is changing with time. You can adjust a half-life of a radionuclide. |

 Home
Home